What is Knowledge Graph?
Brief overview
Previously, was illustrated the general concept of using graph visualization to provide a more intuitive and convenient way for users to navigate and explore the vast amount of information available on the platform.
In that concept, two graphs were used:
- Global graph - aggregates all graphs for each article available on the PrivateAI platform.
- Word graph - local graph that is extracted from the global graph with the selected word at its center.
For now, in order to increase the convenience of global graph search, we propose to implement a Shared context graph which will help users navigate through different levels of graphs.
Shared context graph
Shared context graph - is an alternative representation of word graph.
It works as follows:
- Search of all article graphs containing the selected word
- The found graphs are combined together to form a shared context graph
- To prevent graph overload, when we have a very common/popular word, we divided all these article graphs into batches of N (configurable parameter) to show the combination of only N graphs at once
- User can switch between these batches in the ‘page’ view
This way allows visualizing the overall context in which the selected word occurs and exploring the links between it and other words in the context of different articles.
Examples
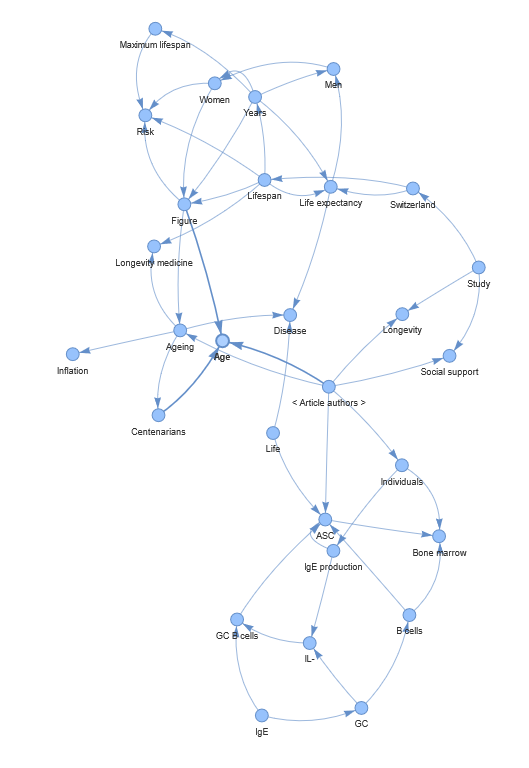
1. Example of shared word graph for word “Age”
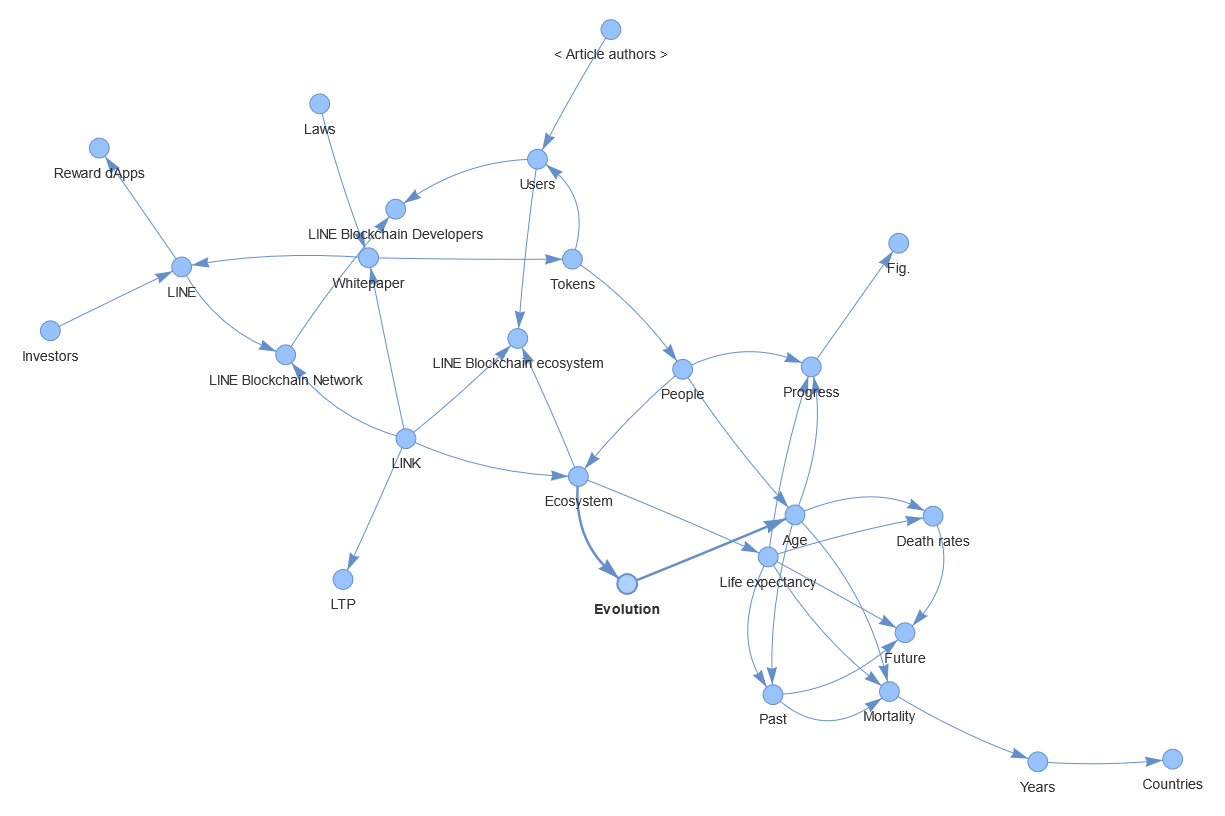
2. Example for word “Evolution”:
Source code
To construct the graph, the shared_word_graph method is used and the following steps are implemented:
- Search for articles containing the word using the count_articles_for_word method;
- Converting the found graphs into networkx format using the to_nxgraph method;
- Counting the number of graphs for further partitioning into batches and sending the info to the frontend;
- User selected a batch (‘page’) of interest, after which the number of the batch is sent to the script that receives it using the get_batch method;
- Calculating of a cross-section of graph indices and combining them by the function built into the networkx library for combining graphs;
- Filtering of the graph by the number of connections of its nodes (low-connected nodes are cut off);
The number of minimum connections is determined by the 'shared_graph_connections’ parameter in the configuration file.
- For debug purposes, the final graph is represented using pyvis library tools.
For more details, the implementation code with comments is shown below:
def count_articles_for_word(self, word):
"""Counts list of graphs with a given word, length of this list and num_batch
num_batch - number of graph batches ("pages")
Args:
word (str): searched word
Returns:
nx_graphs (List[nx.Graph]): list of graphs
num_articles (int): len of list
"""
nx_graphs = []
for graph in self.graphs:
for item in graph[0]:
if item['object'] == word or item['subject'] == word:
nx_graphs.append(self.to_nxgraph(graph[0]))
break
num_articles = len(nx_graphs)
# total number of "pages" of graphs (will be 1..num_batches)
num_batches = math.ceil(num_articles / config['max_graphs_per_word'])
# TODO send num_articles to frontend
return nx_graphs, num_articles
@staticmethod
def get_batch():
"""Get current "page" (graph batch).
Count from 1 to num_batches
Returns:
int: current batch
"""
# TODO receive batch number from frontend
return 1
def shared_word_graph(self, word):
"""Create graph with subgraphs sharing word
Args:
word (str): shared word
Returns:
_type_: _description_
"""
# get list of articles, containing word and its' length
nx_graphs, num_articles = self.count_articles_for_word(word)
current_batch = self.get_batch()
start_index = (current_batch - 1) * config['max_graphs_per_word']
# init first graph in list
united = nx_graphs[start_index]
# Handle exception when last batch has only 1 graph
if num_articles != (current_batch - 1) * config['max_graphs_per_word']:
# Uniting graphs
for nxg in nx_graphs[start_index+1:start_index+config['max_graphs_per_word']]:
united = nx.compose(united, nxg)
# get most connected graph component
main_component = 0
biggest = 0
for component in nx.connected_components(united):
length = len(list(component))
if length > biggest:
biggest = length
main_component = component
main_nodes = list(main_component)
nodes = list(united.nodes)
for node in nodes:
if node not in main_nodes:
united.remove_node(node)
# scale
nodes = list(united.nodes)
top_nodes = []
top_edges = []
for node in nodes:
if node == word:
top_nodes.append(node)
else:
if united.degree(node) >= config['shared_graph_connections']:
top_nodes.append(node)
for node1 in top_nodes:
for node2 in top_nodes:
if node1 != node2:
if [node1, node2] not in top_edges and [node2, node1] not in top_edges:
for path in nx.all_shortest_paths(united, node1, node2):
absense_count = 0
for node in top_nodes:
if node != node1 and node != node2:
if node not in path:
absense_count += 1
if absense_count == len(top_nodes) - 2:
top_edges.append([node1, node2])
break
new = nx.Graph()
new.add_nodes_from(top_nodes)
new.add_edges_from(top_edges)
view = pyvis.network.Network(
directed = True,
height = "900px",
filter_menu = True
)
view.from_nx(new)
view.show("shared_word.html", notebook = False)
# TODO send shared_word graph
@staticmethod
def to_nxgraph(triplets):
"""Converts list of triplets to NX graph
Args:
triplets (List[dict]): list of triplets
Returns:
nx.Graph: nx graph
"""
graph = nx.Graph()
for t in triplets:
graph.add_node(t['subject'])
graph.add_node(t['object'])
graph.add_edge(t['subject'], t['object'], name = t['verb'])
return graph