Graph Formation
Triplet extraction
Step 0:
Step 1:
Step 2:
Step 3:
Step 4:
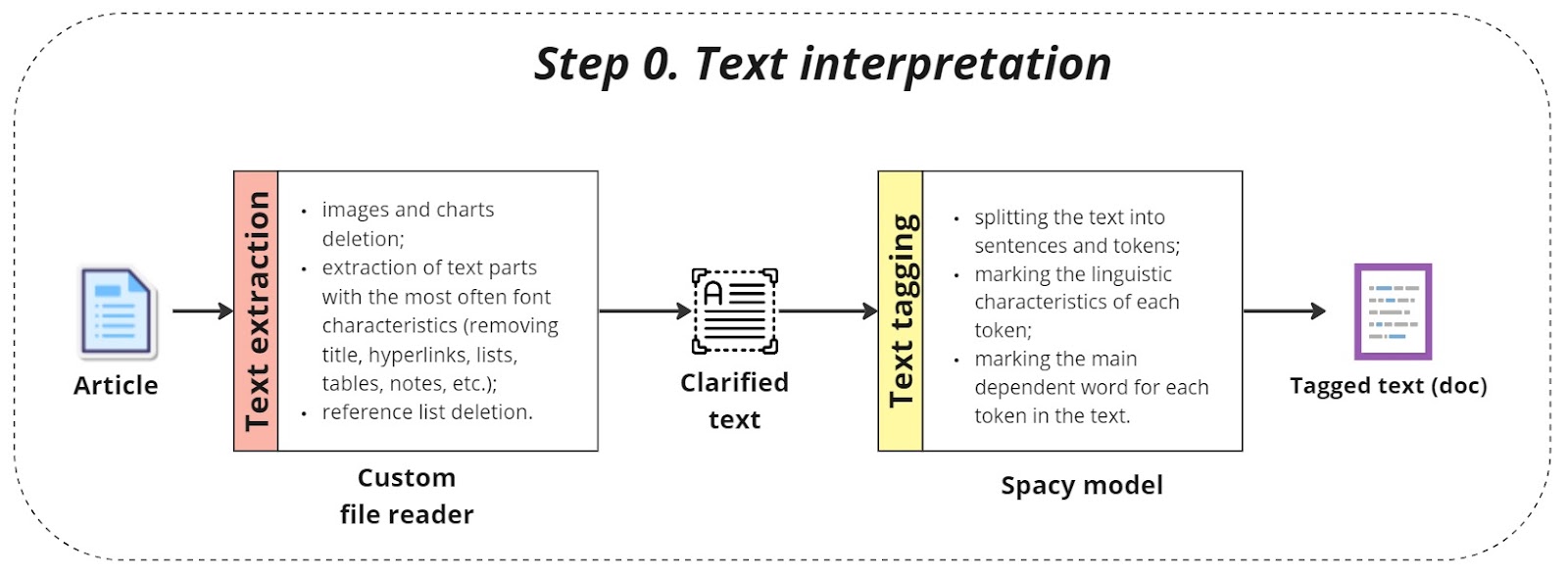
Text interpretation
The first step involves interpreting the raw text data:
-
Custom file reader:
A custom file reader is developed to handle various formats of raw text documents, including PDFs, Word documents, and plain text files. This reader extracts the textual content, ensuring that non-text elements such as images or tables are appropriately handled or excluded.
-
Spacy model processing:
The extracted text is processed using the Spacy natural language processing (NLP) library. Spacy’s pre-trained language models tag the text with parts of speech, named entities, and syntactic dependencies. The output is a doc object that contains detailed linguistic annotations, serving as a foundation for further analysis.
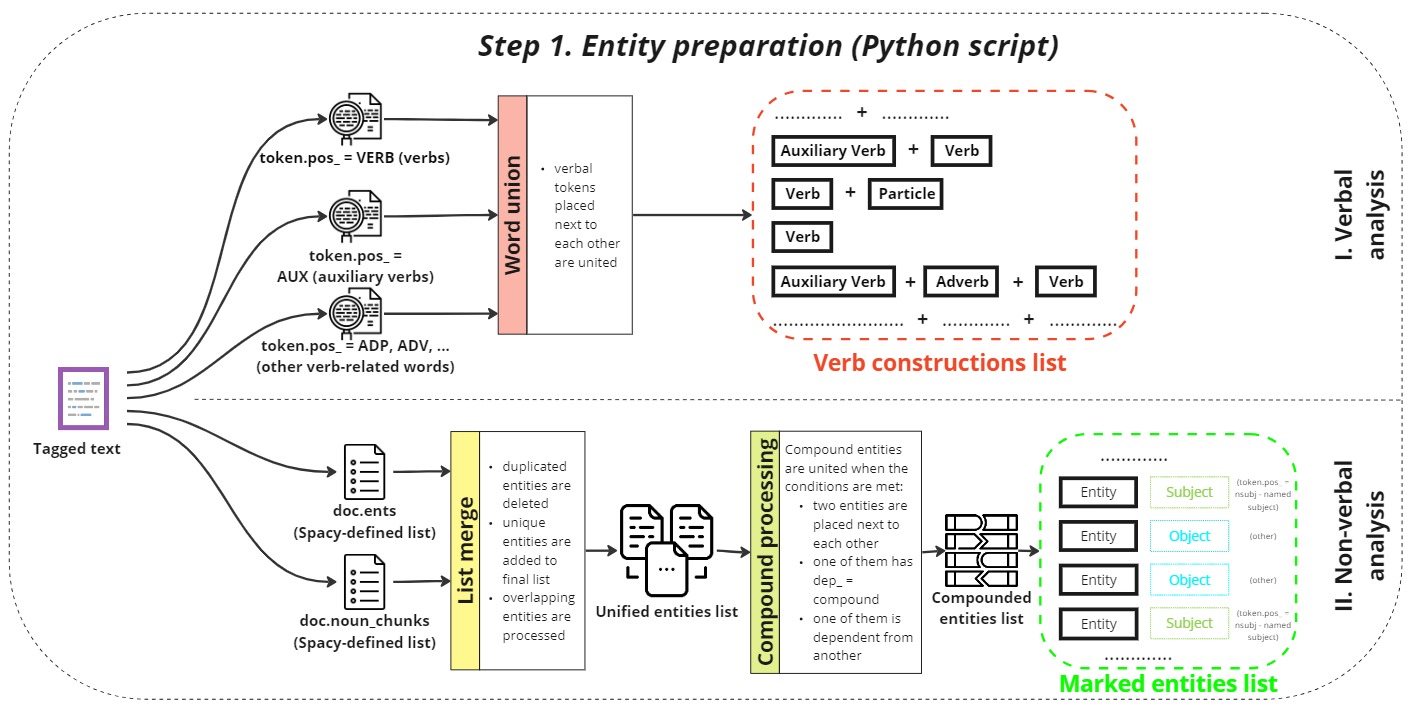
Entity preparation
Next, the tagged text undergoes entity preparation:
-
Verbal and non-verbal analysis:
A Python script performs a detailed analysis of the text to identify both verbal (action words) and non-verbal (descriptive terms) elements. Verbs and their constructions are crucial for understanding actions and events described in the text. Non-verbal elements, such as names, locations, dates, and other significant terms, are marked for entity recognition. -
Output:
The analysis results in two primary outputs: a list of verb constructions and a list of marked entities. These lists are essential for understanding the roles of different elements within the text and their interrelationships.
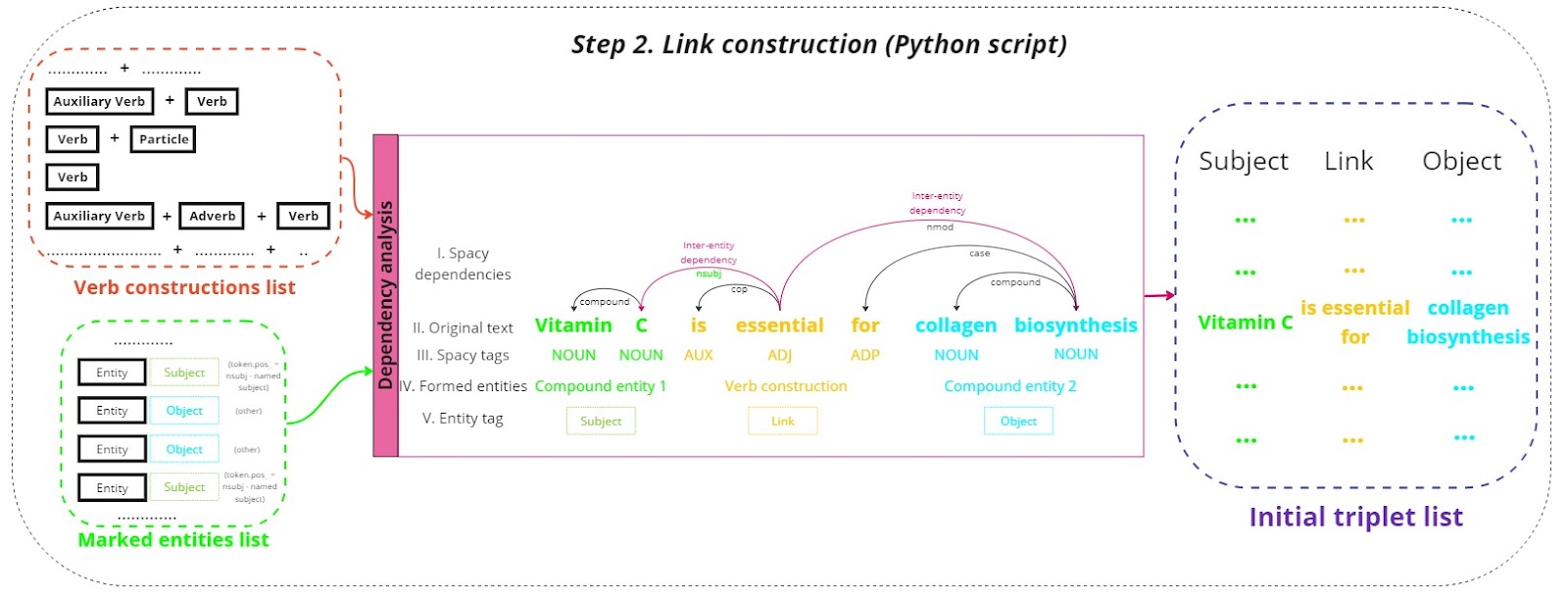
Link construction
The lists of verb constructions and marked entities undergo dependency analysis:
- Dependency analysis:
Dependency parsing examines the grammatical structure of sentences to understand how words relate to each other. This step focuses on identifying subjects, verbs (links), and objects, forming the basic triplet structure [subject, link, object]. The analysis leverages Spacy’s dependency parser to create an initial list of triplets that capture the core relationships within the text. - Initial triplets list:
The initial triplets list forms the raw data for the knowledge graph, encapsulating the key relationships and interactions described in the text. These triplets are the foundational building blocks for constructing the knowledge graph.
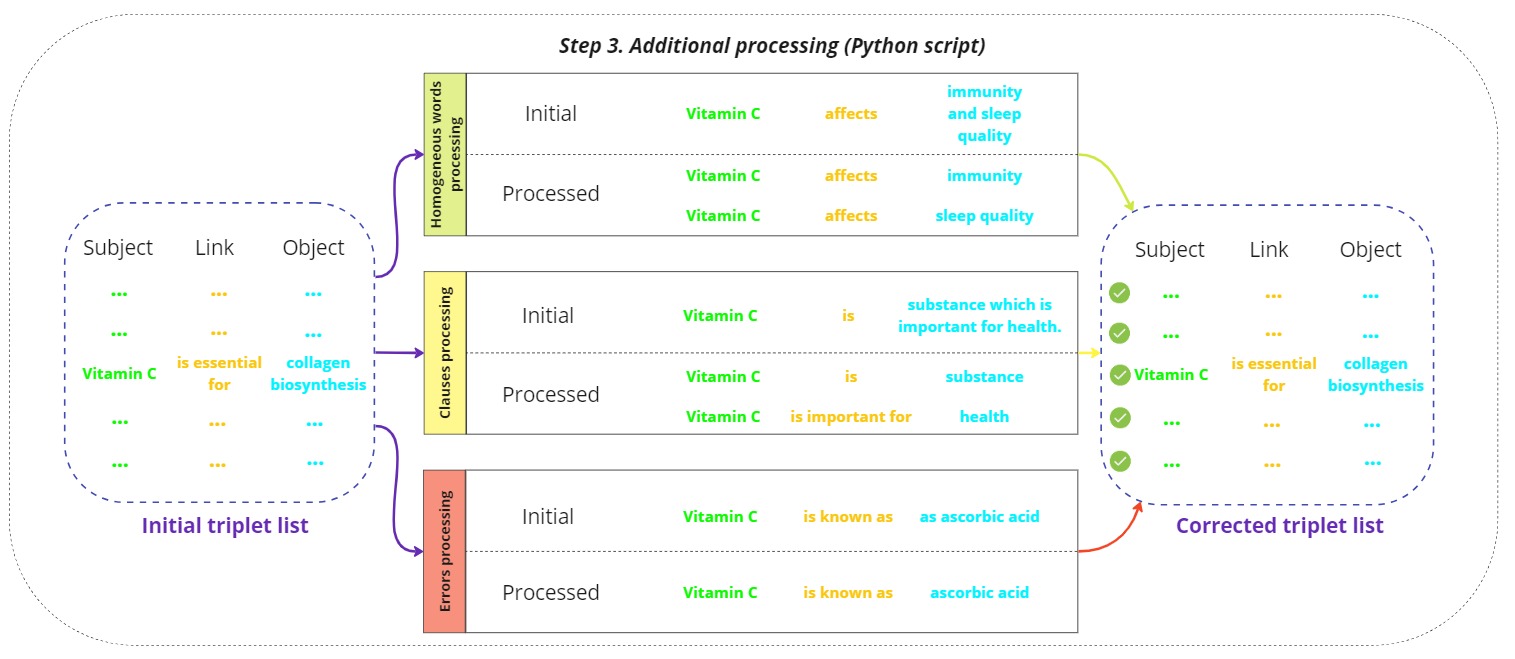
Additional processing
The initial triplets list is refined through several additional processing steps:
-
Error processing:
This step involves identifying and correcting errors in the initial triplets list, such as incorrect relationships or mislabeled entities. Automated scripts and manual reviews ensure that the data is accurate and reliable. -
Clause processing:
Complex sentence structures, such as compound or subordinate clauses, are analyzed to ensure accurate triplet extraction. This step ensures that all relevant relationships are captured, even in complex linguistic constructions.
-
Homogeneous word processing:
Standardizing terms is crucial for maintaining consistency across the triplets. This involves normalizing synonyms, abbreviations, and other variations of terms to a single standard form.
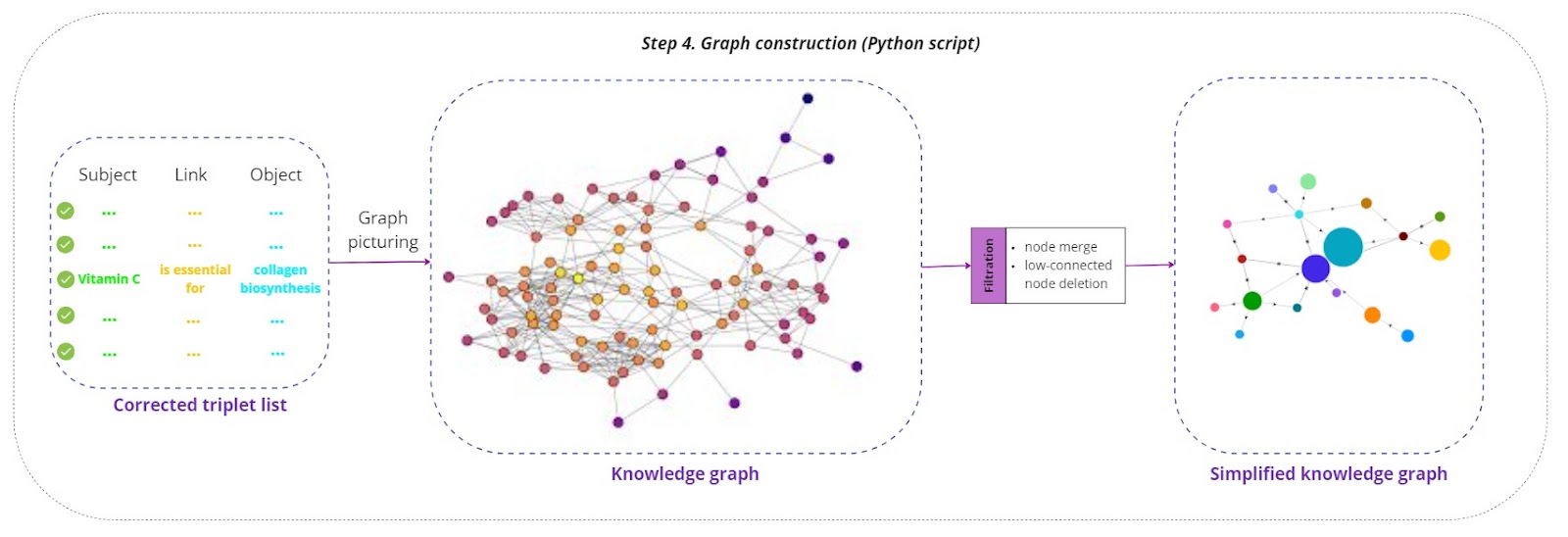
Graph construction
The corrected triplets list is transformed into a knowledge graph:
-
Graph picturing:
Nodes representing subjects and objects are created, and directed edges representing the relationships (links) between them are drawn. Visualization tools such as Gephi or Graphviz can be used to picture the graph, providing a clear and understandable representation.
-
Filtration processes:
- The graph undergoes several filtration processes to enhance its quality:
Node merging: Duplicate nodes representing the same entity are merged to reduce redundancy.
Low-connected node deletion: Nodes with few connections, which may represent noise or irrelevant data, are removed to simplify the graph.
- The graph undergoes several filtration processes to enhance its quality:
Triplets formation
Triplets play a crucial role in the creation of knowledge graphs. They convert unstructured text into a structured format, facilitating better data analysis and insight generation. The process includes several steps:
Named entity recognition (NER)
-
Entity identification:
NER algorithms scan the text to identify and classify entities such as names, locations, organizations, dates, and other significant terms. Spacy’s NER capabilities, supplemented with custom entity recognition models, ensure comprehensive and accurate entity identification.
-
Classification:
Identified entities are classified into predefined categories, which helps in organizing the data and understanding the context of each entity.
Relation extraction (RE)
-
Determining relationships:
RE algorithms analyze the text to determine the relationships between identified entities. This involves identifying the types of interactions or associations, such as “works at,” “located in,” or “part of.”
-
Contextual analysis:
The context of each relationship is analyzed to ensure accuracy. This step may involve co-reference resolution to understand relationships mentioned indirectly or across multiple sentences.
Dependency parsing
-
Syntactic analysis:
Dependency parsing involves a detailed analysis of the grammatical structure of sentences. This step identifies the subjects, verbs, and objects, and understands their grammatical roles and relationships.
-
Understanding relationships:
By analyzing dependencies, the parser can accurately map out how different elements of a sentence relate to each other. This is crucial for forming accurate triplets that reflect the true meaning of the text.
Triplet formation
-
Combining outputs:
The outputs of NER, RE, and dependency parsing are combined to form triplets in the [subject, link, object] format. This involves aligning identified entities and their relationships with the grammatical structure.
-
Triplet standardization:
Triplets are standardized to ensure consistency and clarity.
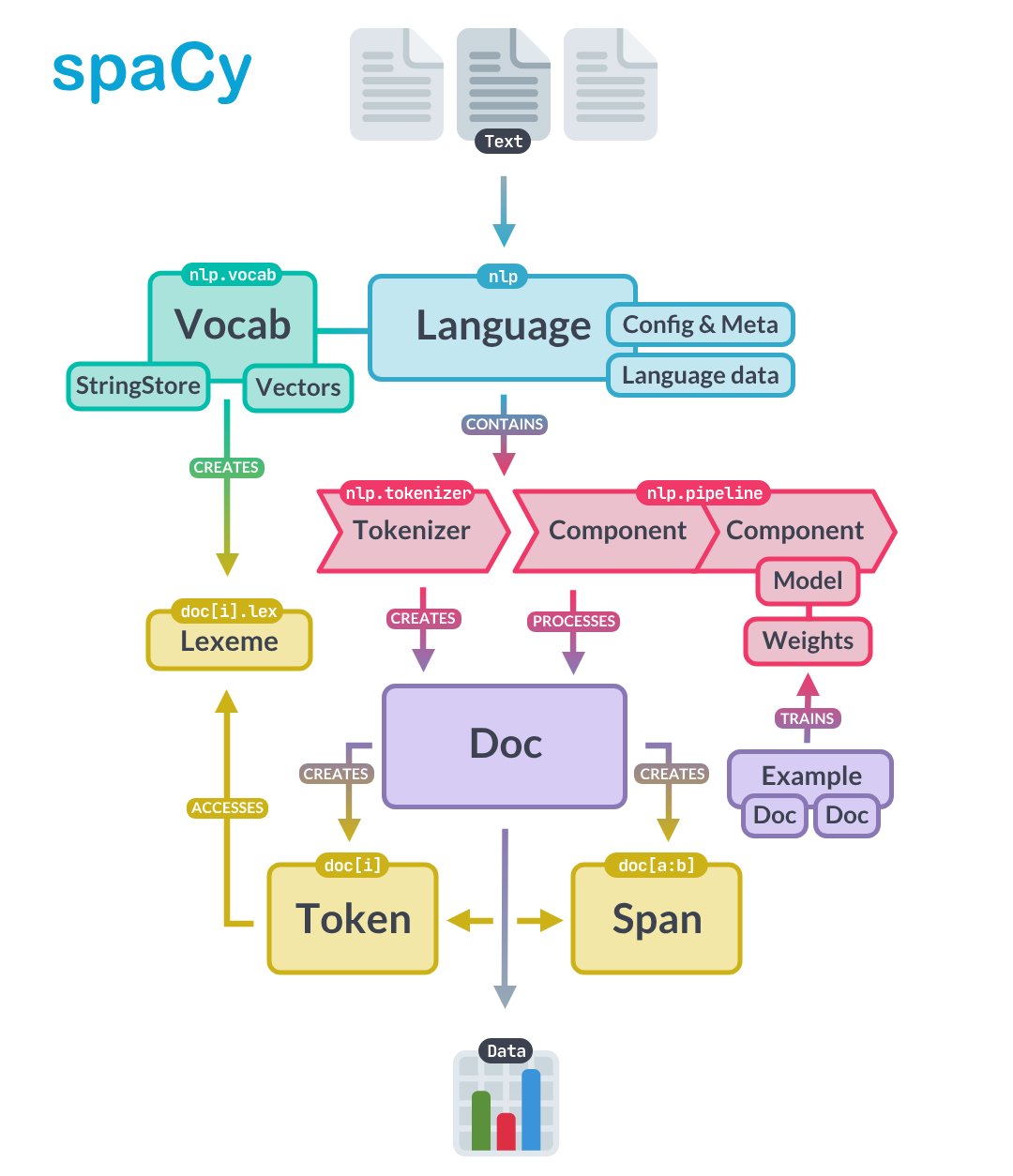
Spacy architecture
General architecture
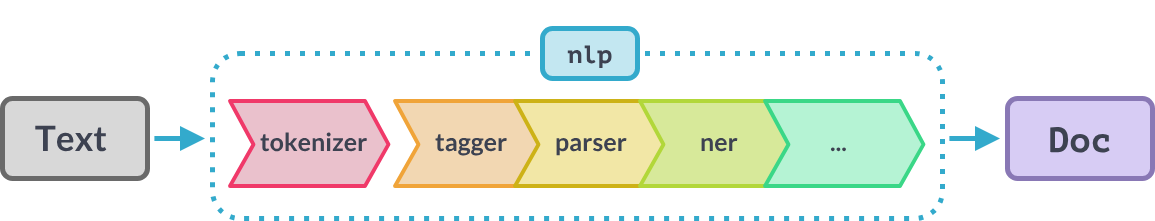
Processing pipeline
PrivateAI quickly overviewed a new conversational assistant called “Le Chat” based on Mistral Large model from the Mistral team.
We tried a few simple prompts to this model regarding our task of triplet extraction and the first impression was quite inspiring.
It shows better results than Mistral 7B in the aspects of triplet list completion and error number. The model processes the texts quickly and requires less detailed prompts to analyze the texts in a needed way.
So, it looks capable of improving our results and we are looking forward to its open API release to test it more comprehensively.