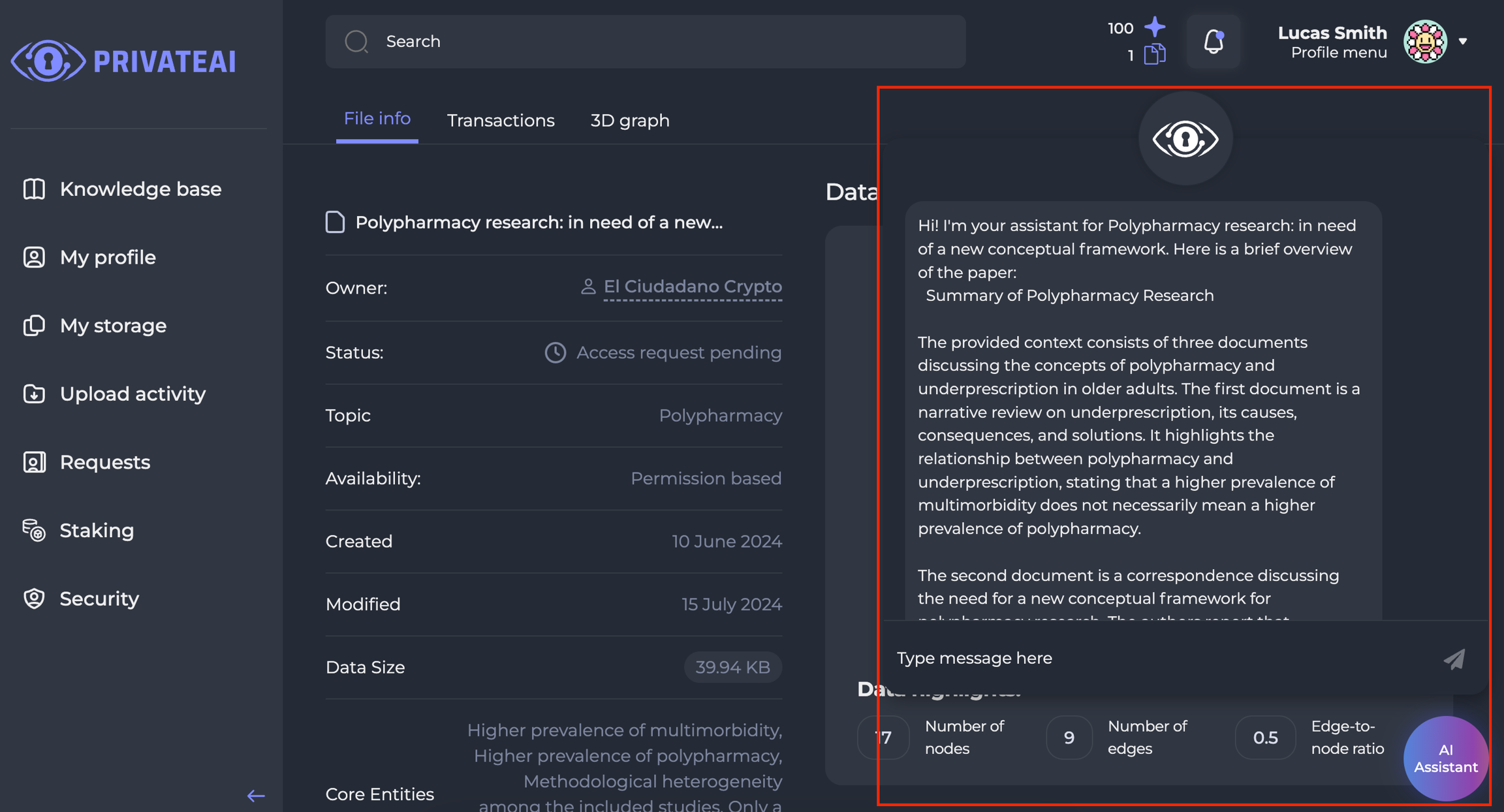
Assistant Interaction Guide
Account guide assistant workspace
User requirements
User roles
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Data searcher | a user who opened a document page to see an overview and discover more about it. |
Use cases diagram
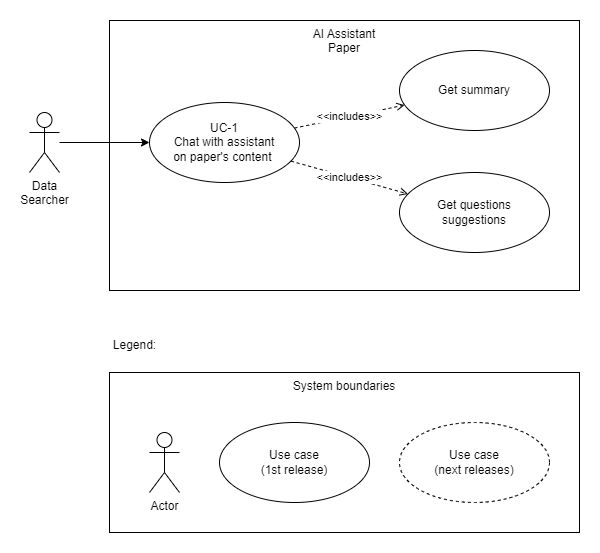
Use cases descriptions
UC 1 - Chat with assistant on paper's content
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Actor | Data Searcher (DS) |
| Description | DS can chat with Assistant. |
| Pre-conditions | Paper is available to view for DS. |
| Main course | DS navigates to the paper’s page. Assistant doesn’t have a dedicated page or tab, and is represented in a pop-up window chat [WF-2] which can be accessed by clicking ‘AI Assistant’ button [WF-1]. User can close pop-up chat at any time. Chat content is stored while the user session is active - so if chat is closed, and then reopened, previous messages are available. If the user signs out, or session is ended by any other reason - chat context is deleted. Dialog with the Assistant Once evoked, Assistant greets the user: <Hi! I'm your assistant for <PaperName>. Here is a brief overview of the paper:> Provides brief overview. Then prints: <Here are some questions that may help you to get better acquainted with the paper:> And provides a set of generated questions - about 3-4. Questions are interactive buttons, so the user can click on each and get Assistant’s response. After that, Assistant prints: <Click on the question above, or type your own in the text field. I'd be happy to help!> And awaits for user input. If a user clicks on a question - it is automatically added to chat as the user's replica, and the assistant answers it. If a user texts their own question, the assistant tries to answer it. [Alt. course 1]
|
| Result | DS evoked Assistant’ pop-up window, and received a paper’s overview, set of questions, and answers for them, or any questions the user has typed into the chat. |
| Alternative courses | Alt.course 1. If the paper is private, Assistant won’t provide any details about the paper content, only brief overview and answers to general questions. |
| Interacting components |
System requirements
Tech concept
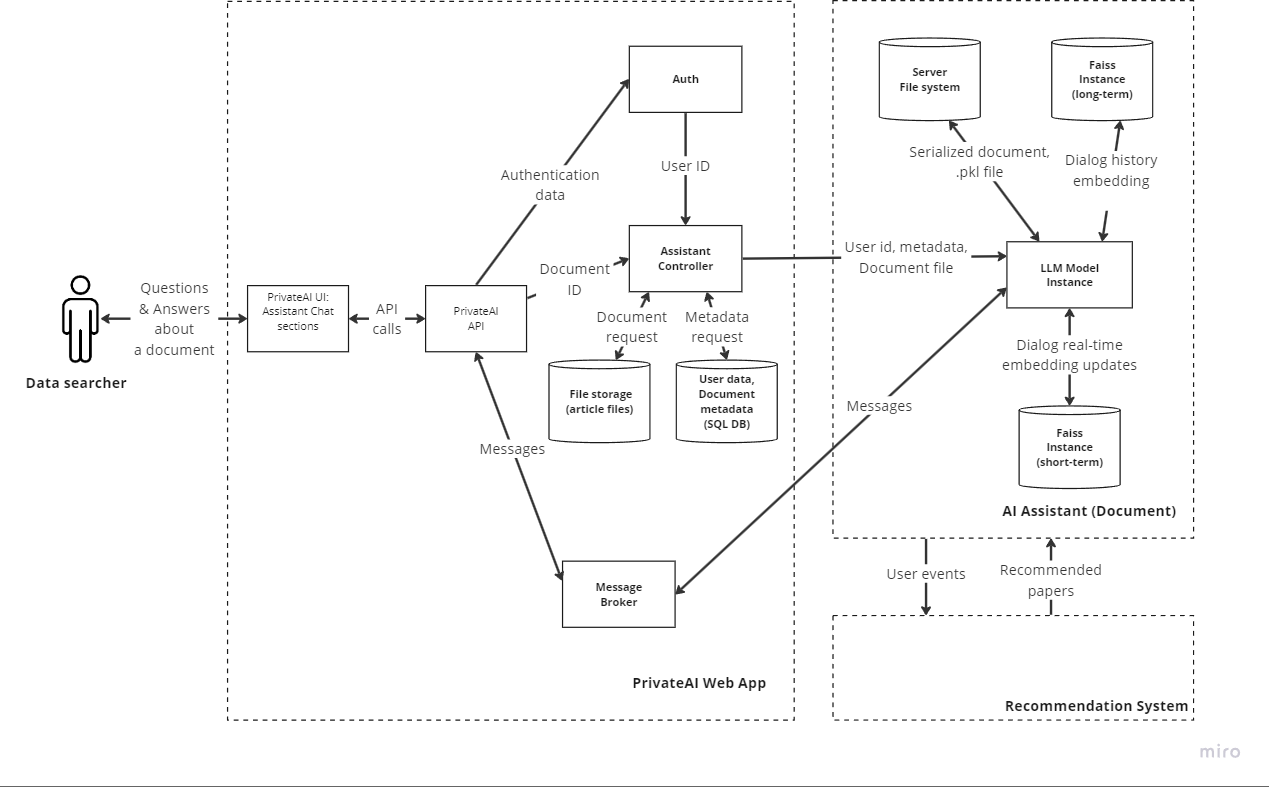
LLM model is located on the PrivateAI server, and works with multiple requests from users.
Each interaction is similar to a session with its own context, which is stored in a long-term Faiss instance.
Model workflow can be described like this:
At the beginning of interaction with a user, model receives user_id, metadata, and document file from PrivateAI backend, this data is pre-processed to create a serialized document file to be further used by the model, and pipeline .pkl file with process configuration.
After that model is prompted by an Assistant Controller module to generate the first 5 questions, and set up with requirements for further communication - all that is stored as a user context in the form of vector embeddings in Faiss instance.
Each user dialog is stored as a context, for a specified period (to be defined). Context is updated along with conversation development, so users can continue communication even after leaving the chat window. In that case the model retrieves vector embeddings from the long-term instance of Faiss, and is able to continue from the interruption point.
Frontend:
- allocates a button to evoke Assistant
- provides a pop-up window with Assistant’s chat.
Backend:
- controls user session,
- provides message brokerage,
- stores chat for a session, and
- provides LLM with paper data for processing.
- provides necessary metadata of the paper.
LLM model:
- generates an overview for each provided paper.
- generates a set of questions which may help user to better understand the paper’s content.
- refuses to talk about details of a private paper.
- refuses to talk about topics unrelated to the paper content.
- is able to restore and continue a chat after some specific period of time.
Scheme
NFR:
NFR1 - If a document is private, the Assistant must not share its private content.
NFR2 - Assistant is content-dependent, meaning it can answer questions only in the current context - i.e. a paper.
AI Assistant - PaperPage UI (to be updated)
Wireframes
WF-1
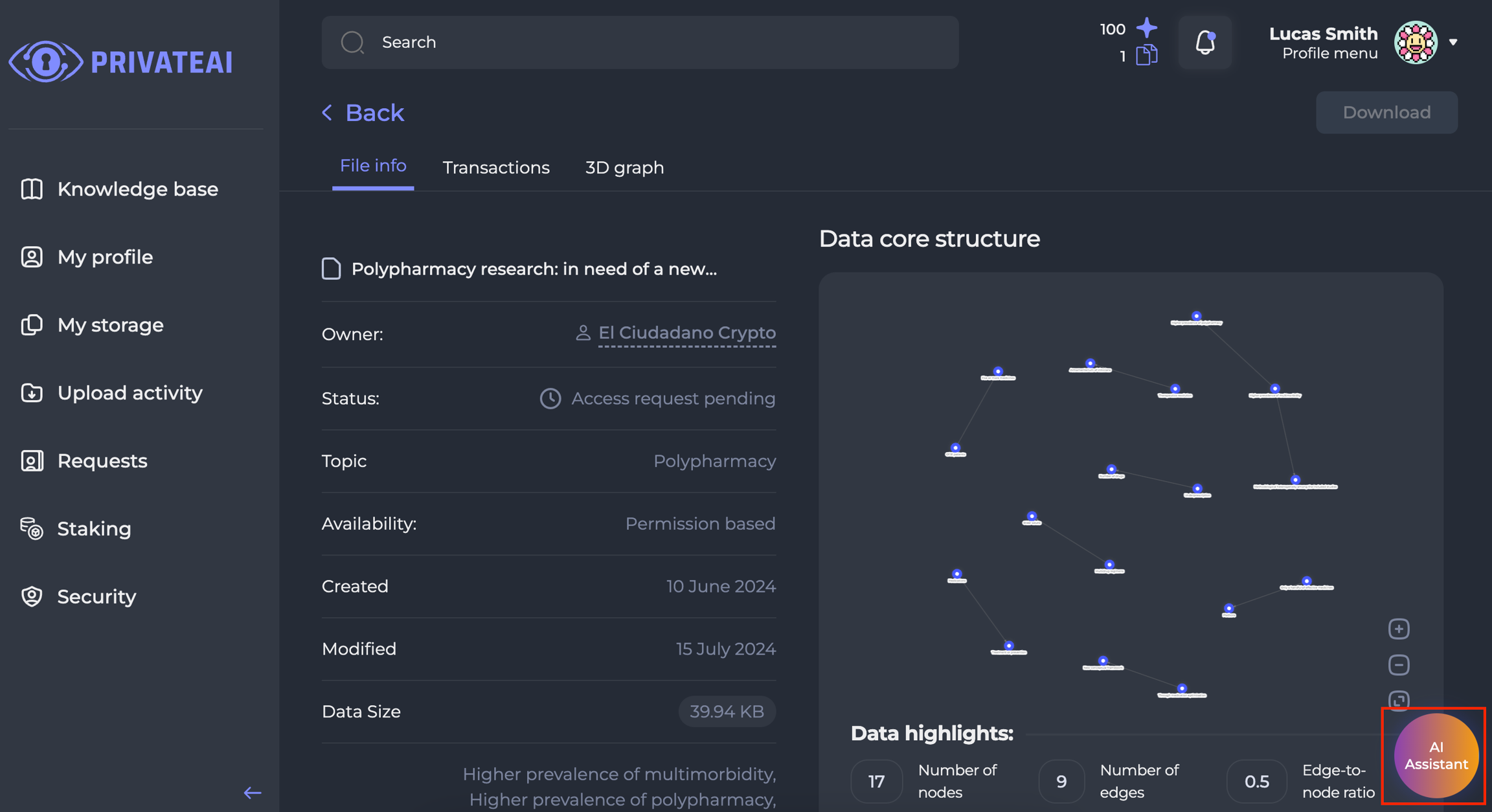
WF-2