The Potential of OpenBioLLM-70B
At PrivateAI.com, we are constantly seeking innovative technologies to enhance our research capabilities. Recently, we've started exploring OpenBioLLM-70B, a cutting-edge large language model specifically designed for biomedical applications. Despite being only a few days old, it has already garnered over 50,000 downloads, showcasing its potential as a valuable tool for medical data processing and research. With its promising capabilities, OpenBioLLM-70B is quickly becoming an essential asset in our quest to advance biomedical research.
Overview of OpenBioLLM-70B
Fine tuned by Saama AI Labs, OpenBioLLM-70B has 70 billion parameters, offering high level of accuracy in understanding and generating biomedical text. Fine-tuned on high-quality biomedical data, this model is particularly good at tasks like clinical note summarization, medical question answering, clinical entity recognition, and de-identification.
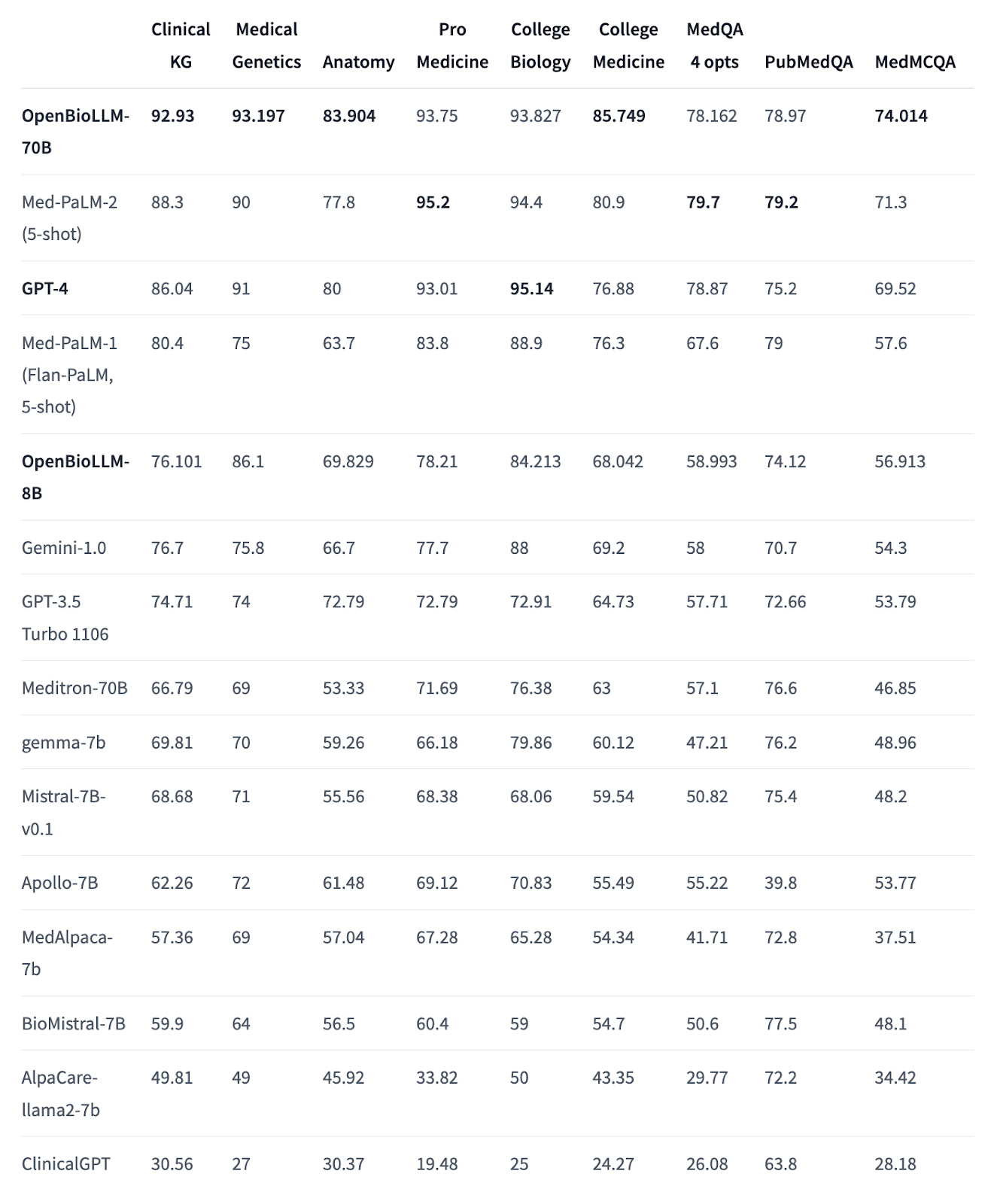
In benchmark tests, it is being compared to similar or larger models:
It has also demonstrated better results compared to larger proprietary & open-source models like GPT-4, Gemini, Meditron-70B, Med-PaLM-1 & Med-PaLM-2 on biomedical benchmarks.
A smaller version, OpenBioLLM-8B is also available, but we will focus on the 70B version since it shows better results according to benchmarks.
Release Details:
- Model Size: 70 billion parameters
- Quantization: Optimized quantized versions (8B version) available Here
- Language(s) (NLP): en
- Developed By: Ankit Pal (Aaditya Ura) from Saama AI Labs
- License: Meta-Llama License
- Fine-tuned from models: Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct
We tested the model on a number of research papers that we typically use. Here's an example:
- Article for testing: Sample 3.pdf
- Example of peer-review: Peer-review Report 3.docx
Applications in Medical Research:
Peer Review Optimizing Scientific Journal review process by article classification
Classifying research articles accurately ensures that high-quality research is disseminated effectively. Journals are often rated using a Q-rating system, where Q1 represents the top 25% of journals, Q2 the next 25%, and so on. These ratings are crucial during the peer review process, as higher-rated journals typically have more rigorous review standards.
OpenBioLLM-70B can assist in classifying articles according to journal quality by analyzing the content and comparing it against criteria for various Q-ratings.
Peer review is a critical step in validating scientific research before it gets published in journals. The model's ability to understand and process medical language makes it a powerful tool for verifying the accuracy and consistency of research articles.
Problem Statement:
A research article claims that Metformin significantly reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases in patients with type 2 diabetes. This claim needs verification against existing literature.
Solution:
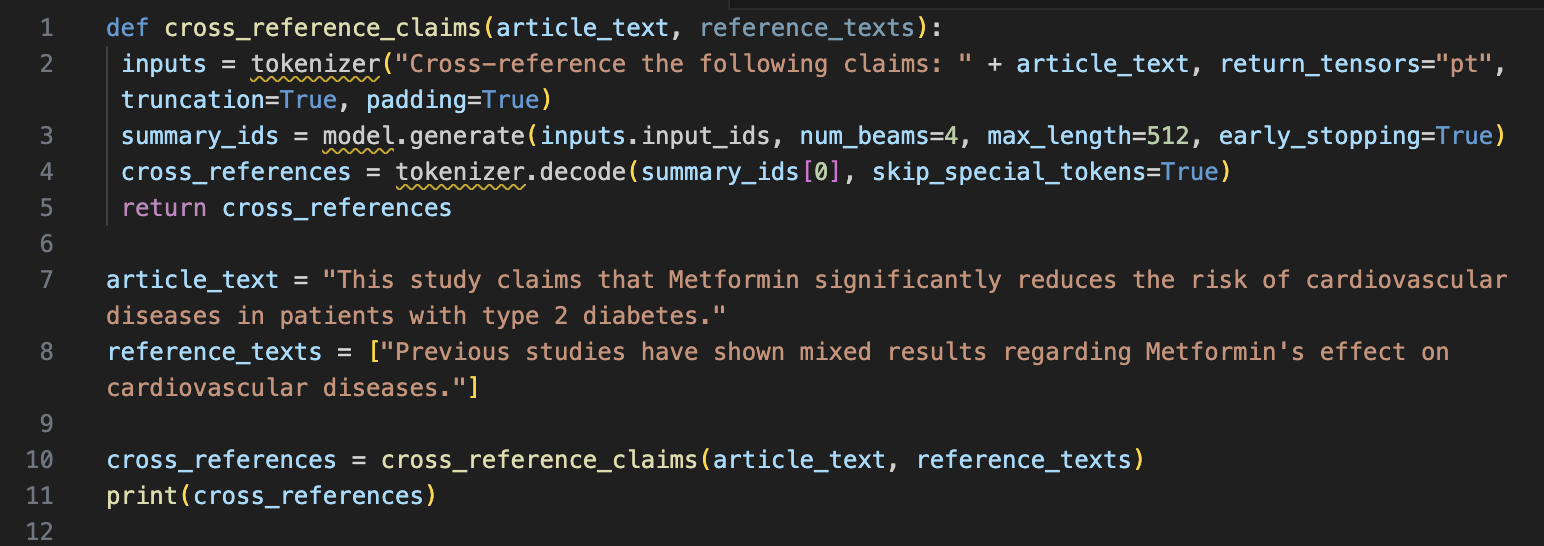
Output:
"The claim that Metformin significantly reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases is not consistently supported by existing studies."
Terminology Normalization and Standardization
Before integrating data into a knowledge graph, we standardize medical terms using ontology dictionaries such as SNOMED CT, ICD, MedDRA and UMLS. This ensures consistent terminology and improves data interoperability.
SNOMED CT
Here's an example how we can normalize terms using SNOMED CT and OpenBioLLM
Problem Statement:
A dataset contains various terms for the same condition, such as "heart attack," "myocardial infarction," and "MI." These terms need to be standardized to "myocardial infarction."
Solution:
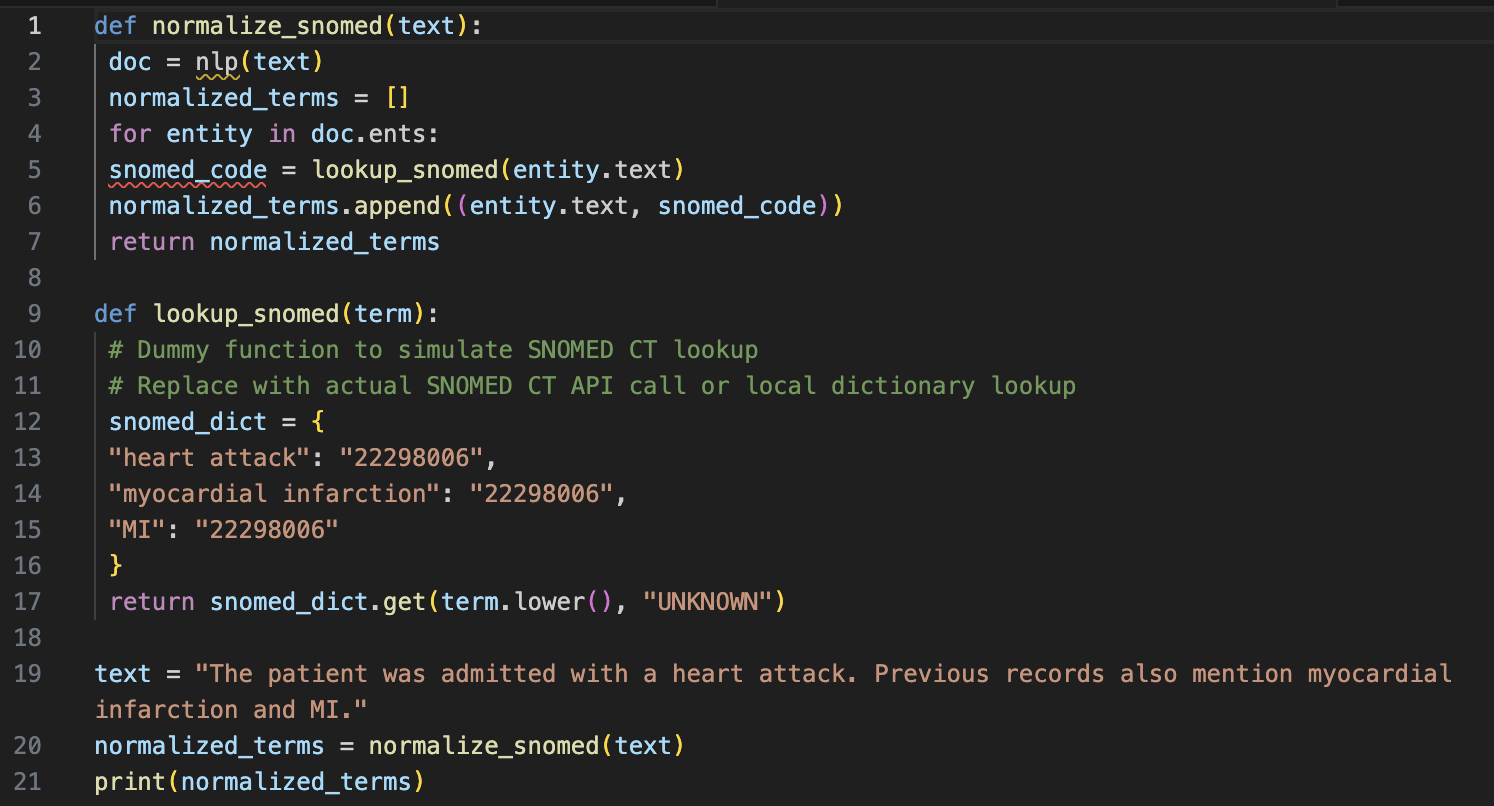
Output:
[('heart attack', '22298006'), ('myocardial infarction', '22298006'), ('MI', '22298006')]
Standardizing with ICD
The ICD coding system is used in healthcare for diagnosing diseases and conditions. Standardizing terms with ICD codes ensures consistency across datasets.
For example, different terms for diabetes, such as "diabetes mellitus", "DM" and "sugar disease" must be standardized using ICD codes.
While OpenBioLLM-70B can be used here, we concluded that use of a combination of SpaCy with the official ICD-11 API will be more effective and faster in this use case. https://icd.who.int/browse/2024-01/mms/en
Building normalized knowledge graphs
Once the terms are normalized, the next step is to build a knowledge graph, which enables advanced data retrieval and analysis. This process is already established and available for testing on https://demo.privateai.com .
Future Potential
As we continue to explore OpenBioLLM-70B, its potential to transform medical research and data processing becomes increasingly clear. From enhancing peer review processes to enabling sophisticated knowledge graph generation, this model is poised to become an indispensable tool for researchers and developers in the biomedical field.
At PrivateAI.com, we’re excited to see how OpenBioLLM-70B will evolve and integrate into various medical applications, driving innovation and improving outcomes in healthcare and life sciences. Stay tuned as we delve deeper into this promising technology and uncover its full capabilities.
For more information on OpenBioLLM-70B, visit its Hugging Face model page.